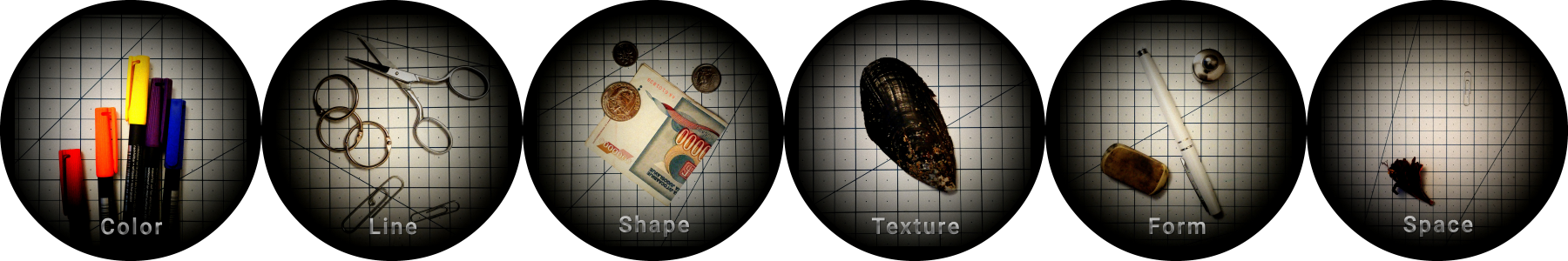
Art Elements
Color, Line, Shape, Texture, Form, Space, Materiality, Markmaking
Six Elements of Art
- Color have three properties:
- hue (particular distinguishable color, e.g. red),
- saturation (chroma or intensity, tints, tones, and shades),
- value (luminosity, lightness or darkness) - the scale from dark (black) through grey till light (white) values.
- Line - 1-dimentional design connecting two points, outline characterized by length and curve:
- actual line, real marks in a composition,
- implied line - suggested by changes in color or texture, or by the edges of shapes.
- Shape - 2-dimensional design encased by lines:
- geometrical (e.g. circle, triangle, rectangle, etc.)
- organic (irregular, e.g. apple, hat, box, etc.).
- Texture - surface quality:
- tactile (real) - physical surface qualities that give tactile feeling by touching and visual effect by reflecting light with variability.
- visual (implied) - gives a sense of texture on a flat surface with lines, shading, and color (simulated, invented, or abstract).
- Form - 3-dimensional object with with perceived volume - height, width, and depth (e.g. sphere, tetrahedron, cube, cylinder. etc.).
- Space - areas within or around the objects and their relationship with the foreground or background:
- positive space - areas of the work with a subject,
- negative space - around or without a subject.
- Materiality: the choice of materials used and how it impacts the work of art.
- Markmaking: the interaction between the artist and the used materials.
Art elements are organized by art principles.